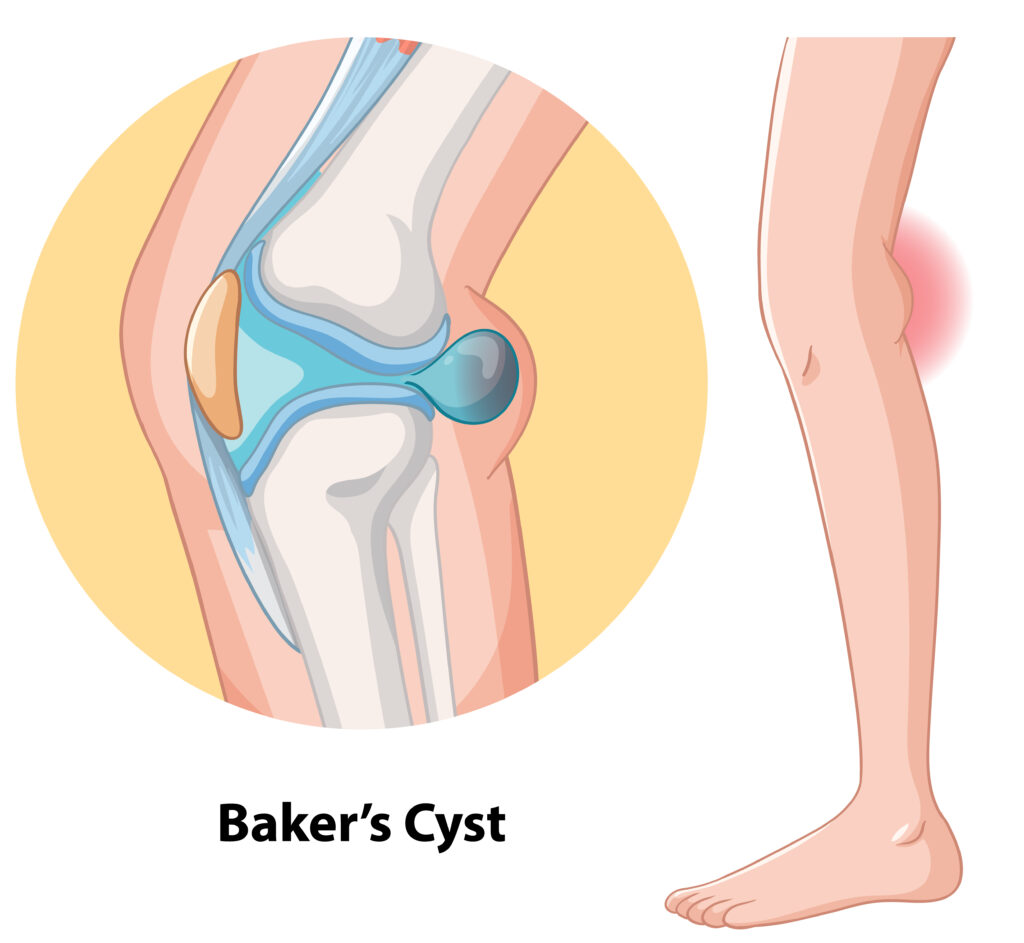
What is a Baker’s Cyst?
A Baker’s cyst, also called a popliteal cyst, is a fluid-filled swelling behind the knee. This swelling can cause discomfort or tightness. Often, people notice it when they bend or straighten their knee. Although it is not usually dangerous, it can be bothersome. According to the CDC, Baker’s cysts often develop due to knee joint problems, such as arthritis or injury.
Common Symptoms of Baker’s Cyst
Many people with a Baker’s cyst may not notice any symptoms at first. However, as the cyst grows, symptoms can appear. For example, you may feel:
In some cases, the cyst can burst. If this happens, fluid may leak into the calf, causing sharp pain, redness, or swelling. If you notice these signs, seek medical help right away.
Causes and Risk Factors
Baker’s cysts form when extra fluid builds up in the knee joint. This fluid is called synovial fluid. It helps the knee move smoothly. But sometimes, the knee makes too much fluid. This can happen because of:
Anyone can get a Baker’s cyst, but some people are at higher risk. For instance, older adults and those with knee arthritis are more likely to develop one. Also, athletes or people with past knee injuries may be at risk.
Diagnosis Methods
Doctors use several ways to diagnose a Baker’s cyst. First, they will ask about your symptoms and check your knee. Next, they may order tests to confirm the diagnosis or rule out other problems. These tests can include:
According to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, these tests help doctors plan the best treatment.
Treatment Options for Baker’s Cyst
Many Baker’s cysts get better on their own. However, treatment can help if you have pain or swelling. Options include:
Medical Treatments
Surgical Treatments
If the cyst keeps coming back or causes severe pain, surgery may be needed. During surgery, the doctor removes the cyst and treats any knee problems. Surgery is usually a last resort if other treatments do not work.
Prevention Tips and Lifestyle Guidance
While you cannot always prevent a Baker’s cyst, you can lower your risk. Here are some helpful tips:
With these steps, you can support knee health and lower your risk of knee swelling or pain.
When to See a Doctor
Sometimes, a Baker’s cyst can be managed at home. However, you should see a doctor if you notice:
These signs could mean a more serious problem, such as a blood clot or infection. Early care can help prevent complications.
Conclusion
Baker’s cyst is a common cause of knee swelling and pain. With the right care, most people find relief. However, it is important to address any knee problems early. Consult an orthopedic specialist at Keyan Clinic for personalized advice on Baker’s cyst and knee pain relief.